Portal:Medicine
The Medicine Portal

Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.
Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of creativity and skill), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an ancient philosopher and physician would apply bloodletting according to the theories of humorism. In recent centuries, since the advent of modern science, most medicine has become a combination of art and science (both basic and applied, under the umbrella of medical science). For example, while stitching technique for sutures is an art learned through practice, knowledge of what happens at the cellular and molecular level in the tissues being stitched arises through science.
Prescientific forms of medicine, now known as traditional medicine or folk medicine, remain commonly used in the absence of scientific medicine and are thus called alternative medicine. Alternative treatments outside of scientific medicine with ethical, safety and efficacy concerns are termed quackery. (Full article...)
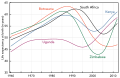
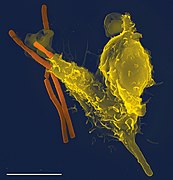
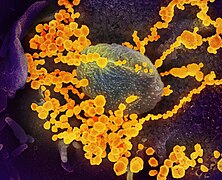
Selected image –

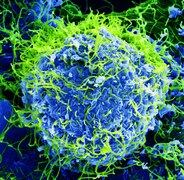
Photo credit: Seldin MF, Shigeta R, Villoslada P, Selmi C, Tuomilehto J, et al. (2006) European Population Substructure: Clustering of Northern and Southern Populations. PLoS Genet 2(9): e143 Fig. 4(b)
WikiProject

Get involved by joining WikiProject Medicine. We discuss collaborations and all manner of issues on our talk page.
Related portals
Did you know –
- ...the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease as a distinct entity were first identified by Emil Kraepelin, and the characteristic neuropathology was first observed by Alois Alzheimer, a German psychiatrist, in 1906? In this sense, the disease was co-discovered by Kraepelin and Alzheimer, who worked in Kraepelin's laboratory. Because of the overwhelming importance Kraepelin attached to finding the neuropathological basis of psychiatric disorders, Kraepelin made the generous decision that the disease would bear Alzheimer's name.
- ...bariatrics is the branch of medicine that deals with the causes, prevention, and treatment of obesity?
- In 2006, according to the World Health Organization, at least 171 million people worldwide suffer from diabetes?
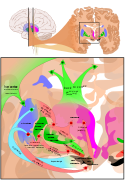
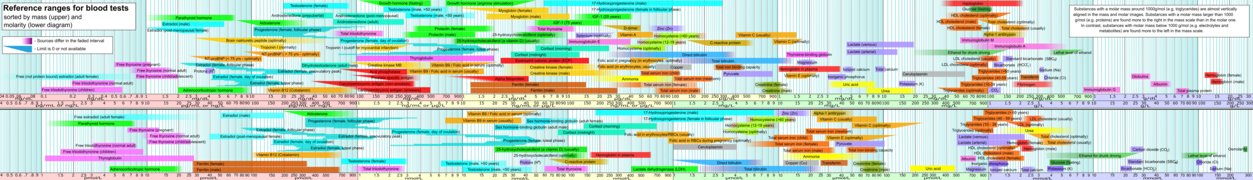
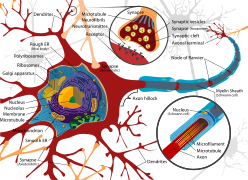
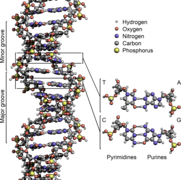
General images –
More Did you know (auto generated)
The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
The time allocated for running scripts has expired.

The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus


































![Image 17Global concentrations of health care resources, as depicted by the number of physicians per 10,000 individuals, by country. Data is sourced from a World Health Statistics 2010, a WHO report.[needs update] (from Health care)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1f/Global_physician_density_map_-_WHO_2010.png/120px-Global_physician_density_map_-_WHO_2010.png)